this post was submitted on 08 Sep 2024
20 points (91.7% liked)
Space
8743 readers
314 users here now
Share & discuss informative content on: Astrophysics, Cosmology, Space Exploration, Planetary Science and Astrobiology.
Rules
- Be respectful and inclusive.
- No harassment, hate speech, or trolling.
- Engage in constructive discussions.
- Share relevant content.
- Follow guidelines and moderators' instructions.
- Use appropriate language and tone.
- Report violations.
- Foster a continuous learning environment.
Picture of the Day
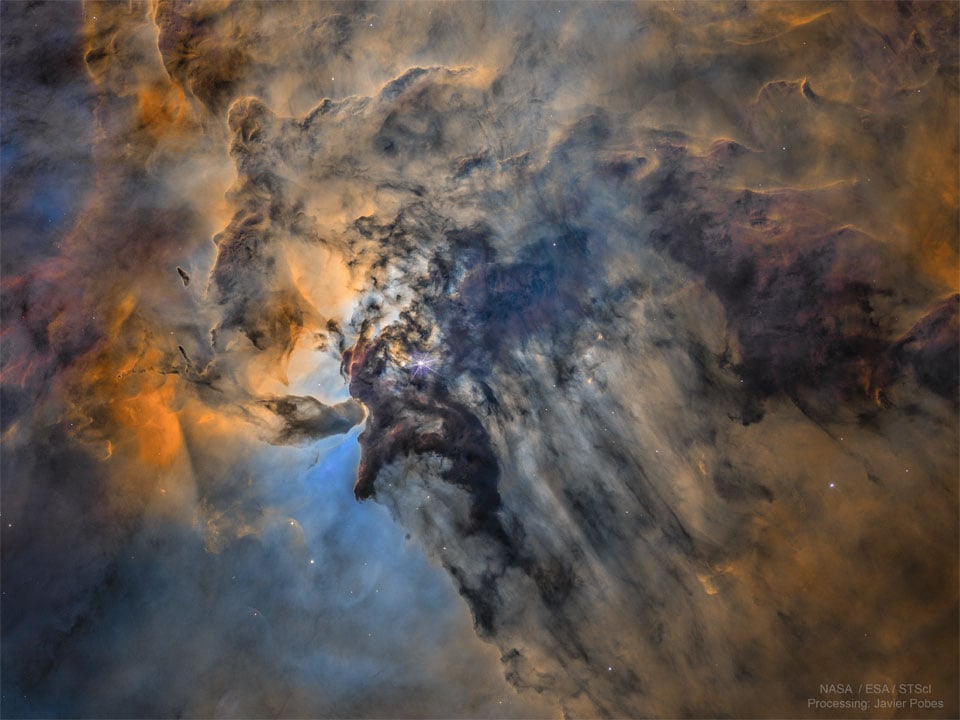 The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
Related Communities
🔭 Science
- !astronomy@mander.xyz
- !curiosityrover@lemmy.world
- !earthscience@mander.xyz
- !esa@feddit.nl
- !nasa@lemmy.world
- !perseverancerover@lemmy.world
- !physics@mander.xyz
- !space@beehaw.org
- !space@lemmy.world
🚀 Engineering
🌌 Art and Photography
Other Cool Links
founded 1 year ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments


Yeah I've been thinking about condensing the water out of the air, too. Problem is: how do you do that? If you use chemical dessication agents, then it's effectively the same as if you let the soil absorb the water from the atmosphere. Just that the soil is already there and you don't need to artificially manufacture dessicants. So it's a bit simpler.
I think you need to compress the air and cool it and you get condensation. I think the advantage of baking the soil would be that the concentration of water vapor would be higher so less energy.
Hmm... maybe the smartest way would be to just build greenhouses and pump compressed air into it. Plants grow, absorb CO2, release oxygen and water. At night you lower insulation and condense excess water out of the air. What is left is a surplus of oxygen. Of course that requires a ton of glass.