this post was submitted on 27 May 2024
978 points (100.0% liked)
196
16423 readers
1698 users here now
Be sure to follow the rule before you head out.
Rule: You must post before you leave.
founded 1 year ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
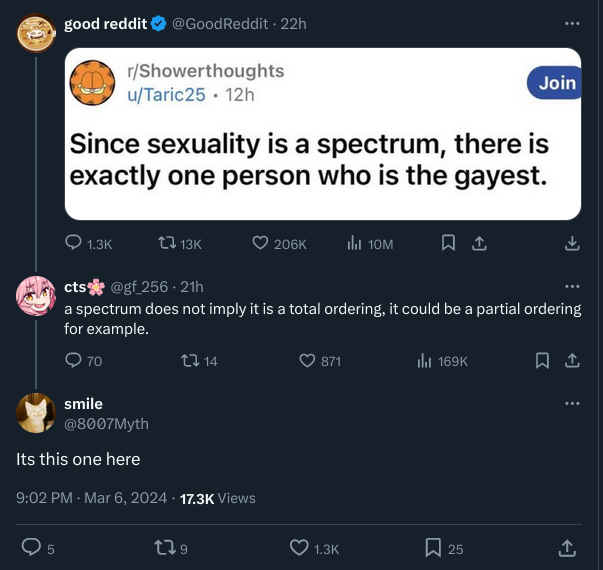
But maximums are only guaranteed to be represented by a unique element in in total orderings.
Edit: also, infinite sets might not necessarily contain an element of their maximum value.
There are demonstrably not infinite humans alive at the same time though.
Are you suggesting gayness is measured in number of humans?
No, but each individual human is assigned identically one gayness value, therefore the number of values we must sort is equal to the number of living humans
But the possible number of outcomes is not limited by the subset of living humans. While we may have a currently highest number that doesn’t mean it IS the highest possible, nor that there is exactly one of them.
I would argue you can only be gay if you're alive, so you only need to compare living people, the theoretical maximum doesn't matter, only the actual maximum of a finite number.
Agreed. It might be a shared gold medal.
It is true that the gayest person currently alive, the gayest person ever in history, and the gayest person who could possibly exist may well exhibit three different levels of gayness; however, I believe that, were one sufficiently determined, it would be possible to find all three.
I'd argue each of has a gay expression, Gayness can absolutely change in accordance with time.
Obviously not
Okay, so Earth exists. This means for a set volume of space (say about the size of the solar system) there is some positive probability that it contains a planet that is indistinguishable from earth. Let's assume the universe is infinite. If we can search an arbitrary volume instantly, our probability for finding a duplicate of earth approaches 1 as our volume increases. This means the probability we will never find a duplicate of earth is exactly 0, which means that we will find a duplicate upon searching a finite volume. Since in our hypothetical the search is instant, we can perform this search again, locating a second duplicate of earth. Following this process, we can locate an arbitrary number of perfect earth duplicates in a finite ammount of time. This means that if Earth arose from natural processes in an infinite universe, there are infinitely many exact duplicates of earth with life that includes specimens genetically identical to humans.
This implies that there is no one gayest person in the universe.
Eh.
You're starting from the assumption that the universe is infinite, and conclude that there is no maximum because the universe is infinite.
Sorry for being this blunt, but that's intellectually boring.
Most of the entertainment comes from the non-obvious corollaries of the intermediate results. For example, every person has infinitely many perfect yet distinct copies that are identical right down to personal histories.
There's more, if you care to take the time to think about them. I was just using the conversation as an excuse to expose more people to the implication.
There are infinities without repetition. Usually the proofs for the stuff you describe assumes finite possibilities.
Please elaborate.
There are an infinite number of numbers between 0 and 1, and yet there is no repetition. Pi and other irrational numbers are infinite yet non-repeating. I wish I knew the name for this kind of thing because I'm sure it's been discussed in philosophy (a kind of opposite, eternal recurrence, has been discussed a lot).
I don't think anyone knows enough about the universe to say whether or not there is infinite variety in macroscopic stuff, so I don't think anything can be ruled out.
There are finitely many particles in the observable universe (that is to say, an infinite number will not fit), and a finite granularity to discern the position of those particles. That means there are finitely many configurations of particles within the volume of the observable universe.
Therefore, there are finitely many discernable things, so in a meaningful sense we can say with confidence that there's a finite variety of macroscopic things.
Whether or not an infinite number of particles will fit or not is not important, no ? I'm not sure what you mean by finite granularity. There is no "grid", space is continuous, the planck length and the fact that push on each other doesn't really factor in. By virtue of space being continuous and particles being finite, means you can configure stuff in infinite ways.
Edit: Not quoting you with the reference to a grid. I know that's not what you mean.
Are you aware of the plank length? It's the distance less than which which we can no longer determine if 2 things are any closer.
Don't worry, I understand.
Yes, but distance is still continuous, a minimum measurable distance (between stuff) doesn't make space granular. I suppose there might be a minimum measurably meaningful number of configurations, but I'm not super convinced.
My claim accounts for the possibility that the distances of particles may physically differ by amounts more granular than a plank length. My statement was that they are indiscernable. There are infinite copys of every person more closely identical than the two most similar identical twins. So closely identical that no physically possible device could ever distinguish between them. We cannot know if space is continuous. We simply know that if it is not continuous, it is of granularity as fine or finer than the plank length. So there is a meaningful sense in which there are finitely many macroscopic objects.
So far nothing in the universe has shown to be infinite, hence any material representation of Gabriel's Horn can be painted since paint has a thickness.
The Plank length is the shortest possible distance between two material points. Though at that scale even vacuum is tempestuous.