This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Bird flu has been detected in a pig in the US. Why does that matter?

C Raina MacIntyre, UNSW Sydney and Haley Stone, UNSW Sydney
The United States Department of Agriculture last week reported that a pig on a backyard farm in Oregon was infected with bird flu.
As the bird flu situation has evolved, we’ve heard about the A/H5N1 strain of the virus infecting a range of animals, including a variety of birds, wild animals and dairy cattle.
Fortunately, we haven’t seen any sustained spread between humans at this stage. But the detection of the virus in a pig marks a worrying development in the trajectory of this virus.
How did we get here?
The most concerning type of bird flu currently circulating is clade 2.3.4.4b of A/H5N1, a strain of influenza A.
Since 2020, A/H5N1 2.3.4.4b has spread to a vast range of birds, wild animals and farm animals that have never been infected with bird flu before.
While Europe is a hotspot for A/H5N1, attention is currently focused on the US. Dairy cattle were infected for the first time in 2024, with more than 400 herds affected across at least 14 US states.

Bird flu has enormous impacts on farming and commercial food production, because infected poultry flocks have to be culled, and infected cows can result in contaminated diary products. That said, pasteurisation should make milk safe to drink.
While farmers have suffered major losses due to H5N1 bird flu, it also has the potential to mutate to cause a human pandemic.
Birds and humans have different types of receptors in their respiratory tract that flu viruses attach to, like a lock (receptors) and key (virus). The attachment of the virus allows it to invade a cell and the body and cause illness. Avian flu viruses are adapted to birds, and spread easily among birds, but not in humans.
So far, human cases have mainly occurred in people who have been in close contact with infected farm animals or birds. In the US, most have been farm workers.
The concern is that the virus will mutate and adapt to humans. One of the key steps for this to happen would be a shift in the virus’ affinity from the bird receptors to those found in the human respiratory tract. In other words, if the virus’ “key” mutated to better fit with the human “lock”.
A recent study of a sample of A/H5N1 2.3.4.4b from an infected human had worrying findings, identifying mutations in the virus with the potential to increase transmission between human hosts.
Why are pigs a problem?
A human pandemic strain of influenza can arise in several ways. One involves close contact between humans and animals infected with their own specific flu viruses, creating opportunities for genetic mixing between avian and human viruses.
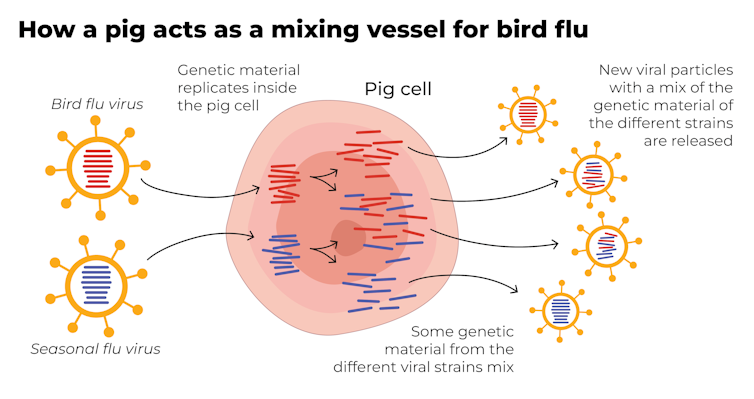
Pigs are the ideal genetic mixing vessel to generate a human pandemic influenza strain, because they have receptors in their respiratory tracts which both avian and human flu viruses can bind to.
This means pigs can be infected with a bird flu virus and a human flu virus at the same time. These viruses can exchange genetic material to mutate and become easily transmissible in humans.
The Conversation, CC BY-SA
Interestingly, in the past pigs were less susceptible to A/H5N1 viruses. However, the virus has recently mutated to infect pigs more readily.
In the recent case in Oregon, A/H5N1 was detected in a pig on a non-commercial farm after an outbreak occurred among the poultry housed on the same farm. This strain of A/H5N1 was from wild birds, not the one that is widespread in US dairy cows.
The infection of a pig is a warning. If the virus enters commercial piggeries, it would create a far greater level of risk of a pandemic, especially as the US goes into winter, when human seasonal flu starts to rise.

How can we mitigate the risk?
Surveillance is key to early detection of a possible pandemic. This includes comprehensive testing and reporting of infections in birds and animals, alongside financial compensation and support measures for farmers to encourage timely reporting.
Strengthening global influenza surveillance is crucial, as unusual spikes in pneumonia and severe respiratory illnesses could signal a human pandemic. Our EPIWATCH system looks for early warnings of such activity, which can speed up vaccine development.
If a cluster of human cases occurs, and influenza A is detected, further testing (called subtyping) is essential to ascertain whether it’s a seasonal strain, an avian strain from a spillover event, or a novel pandemic strain.
Early identification can prevent a pandemic. Any delay in identifying an emerging pandemic strain enables the virus to spread widely across international borders.
Australia’s first human case of A/H5N1 occurred in a child who acquired the infection while travelling in India, and was hospitalised with illness in March 2024. At the time, testing revealed Influenza A (which could be seasonal flu or avian flu), but subtyping to identify A/H5N1 was delayed.
This kind of delay can be costly if a human-transmissible A/H5N1 arises and is assumed to be seasonal flu because the test is positive for influenza A. Only about 5% of tests positive for influenza A are subtyped further in Australia and most countries.
In light of the current situation, there should be a low threshold for subtyping influenza A strains in humans. Rapid tests which can distinguish between seasonal and H5 influenza A are emerging, and should form part of governments’ pandemic preparedness.
A higher risk than ever before
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that the current risk posed by H5N1 to the general public remains low.
But with H5N1 now able to infect pigs, and showing worrying mutations for human adaptation, the level of risk has increased. Given the virus is so widespread in animals and birds, the statistical probability of a pandemic arising is higher than ever before.
The good news is, we are better prepared for an influenza pandemic than other pandemics, because vaccines can be made in the same way as seasonal flu vaccines. As soon as the genome of a pandemic influenza virus is known, the vaccines can be updated to match it.
Partially matched vaccines are already available, and some countries such as Finland are vaccinating high-risk farm workers.
C Raina MacIntyre, Professor of Global Biosecurity, NHMRC L3 Research Fellow, Head, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute, UNSW Sydney and Haley Stone, Research Associate, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute & CRUISE lab, Computer Science and Engineering, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.







Stop weather data collection in one part of the planet. That'll stop the global warming believers. /s
Crops grow faster if you decree the weather is perfect. The best weather.