this post was submitted on 22 Sep 2024
50 points (96.3% liked)
Space
8743 readers
314 users here now
Share & discuss informative content on: Astrophysics, Cosmology, Space Exploration, Planetary Science and Astrobiology.
Rules
- Be respectful and inclusive.
- No harassment, hate speech, or trolling.
- Engage in constructive discussions.
- Share relevant content.
- Follow guidelines and moderators' instructions.
- Use appropriate language and tone.
- Report violations.
- Foster a continuous learning environment.
Picture of the Day
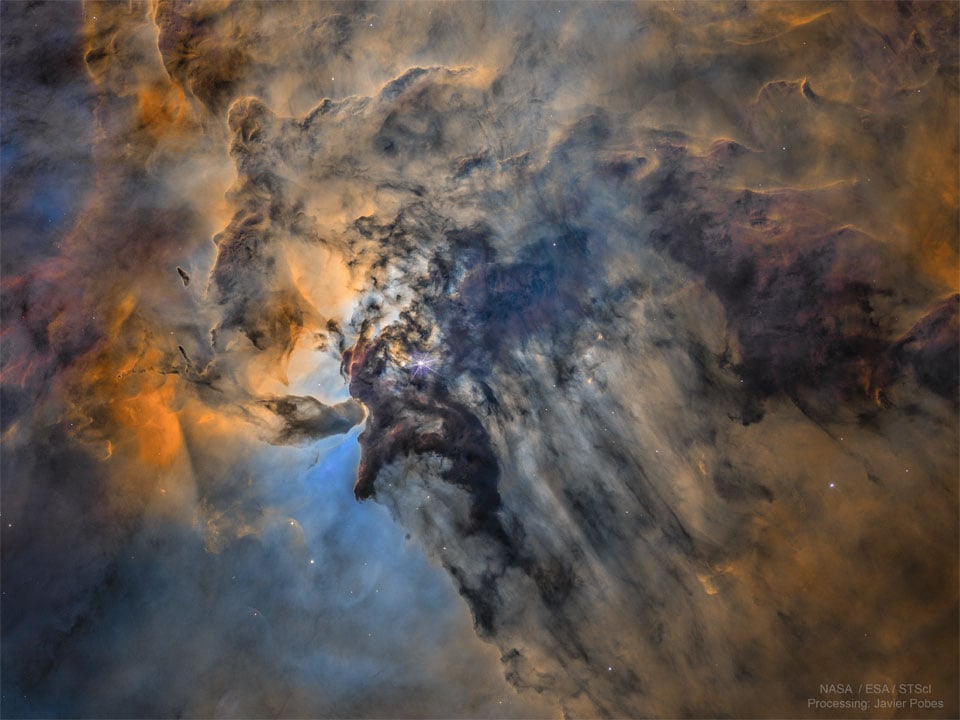 The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
Related Communities
🔭 Science
- !astronomy@mander.xyz
- !curiosityrover@lemmy.world
- !earthscience@mander.xyz
- !esa@feddit.nl
- !nasa@lemmy.world
- !perseverancerover@lemmy.world
- !physics@mander.xyz
- !space@beehaw.org
- !space@lemmy.world
🚀 Engineering
🌌 Art and Photography
Other Cool Links
founded 1 year ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments

Well, we would choose a specific thing or group of things close together that we want to look at, and launch for that specific thing.
Once done with the primary mission, all the neat things we pick up on while getting the primary taken care of can be looked at.
That's what we already do with space things anyway. It just happens that most of the telescopes we've built to date were more general purpose. Hubble has/d a much broader scope than JWST, but you can't discount either for their value.
I'm probably not making my point very well, but basically we wouldn't just send it somewhere arbitrarily (which I'm sure you already know, but some might not think about that) and hope to find something cool, we will intentionally target something and then go from there.
We technically have the tech to do this, what we lack, is species cohesion and cooperation to lower the effective costs of said endeavor, and the patience to wait for it to set up. Being so far from the inner planets means it's gonna take a long time to get in position.